AI Adoption Guide: From Pilot to Full Rollout
How to move beyond early adopters and unlock your organization’s full potential?
The adoption of generative AI tools such as ChatGPT and Microsoft Copilot promises massive productivity gains across industries. But after a successful pilot with enthusiastic users, organizations often hit a wall: the broader workforce isn’t as quick to follow. This guide explains why – and what you can do about it.
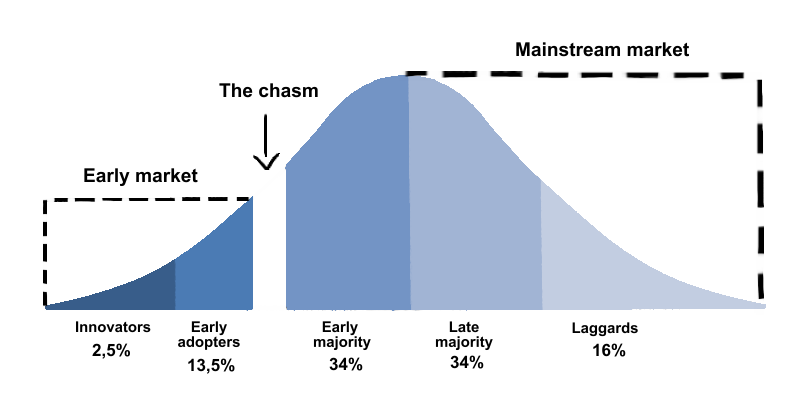
Model of the technology adoption lifecycle.
Understanding the Technology Adoption Cycle
The Technology Adoption Lifecycle divides users into five groups: Innovators, Early Adopters, Early Majority, Late Majority and Laggards.
Most AI pilots are run with Innovators and Early Adopters—those who are curious, self-driven, and often experimenting with AI tools even before official rollout. This makes pilots seem more successful than they might be across the entire company.
The Early Majority and beyond are harder to train. They’re less excited by new tools and need more structured, hands-on guidance to see value.
Why Online Training Falls Short for the Majority
Online and on-demand training can be effective for enthusiastic users. But for the broader workforce, they come with key downsides:
Low engagement: Participants often multitask—checking email, attending meetings, or browsing their phones.
Poor completion rates: Assignments aren’t done, videos aren’t watched, and learning is shallow.
Lack of immediate help: When something doesn’t work, frustration builds. Without fast support, many give up.
No visibility for the trainer: It’s hard to spot who’s stuck or disengaged in a digital session.
Visualizer by Yamu_Jay on Pixabay.
The Power of In-Person Training
Live, in-person trainings dramatically increase the effectiveness of AI adoption. Here’s why:
Higher Engagement
People are present—less likely to multitask or zone out.
The trainer can command the room’s attention and adapt dynamically to reactions and energy.
More Active Participation
Assignments are more likely to be completed during the session.
Challenges can be addressed on the spot, removing blockers instantly.
Real-Time Support
The trainer can see who is stuck or hesitant and step in.
Participants are more likely to raise their hands and ask questions.
Social Learning
People feel more comfortable asking for help in small group settings.
Trainers can “seed” the room by enlisting a few participants to ask questions early, encouraging others to join in.
Use Case Discovery
Set aside time during the session for participants to work in small groups to identify how AI can help them in their specific roles. This transforms the training from abstract learning to immediate practical value.
Conclusion: Design for the Real World
To ensure generative AI becomes a tool your whole workforce embraces—not just the early enthusiasts—you need to go beyond pilots and meet people where they are. That means:
Recognizing that most workers won’t self-train.
Investing in high-impact, in-person training.
Creating room for discovery, dialogue, and direct support.
At AiSkillSet, we’ve built our training model around this reality. We've identified that the biggest challenge is not training the eager few—it’s enabling the majority.
That’s why we specialize in in-person trainings at the client’s location, delivered in small group settings of 10–30 participants. This setting allows us to offer individual attention, support, and real-time feedback, which dramatically improves engagement and retention.
We offer:
Tool-specific trainings on Microsoft Copilot, ChatGPT, and other key AI tools.
Role-specific trainings for functions such as financial administration, marketing, HR, and more.
Our goal is to ensure that every participant leaves with clear ideas of how AI can support their specific day-to-day work—and the confidence to start using it right away.